この記事では、GridDBデータベースから自然言語クエリを使用して情報を取得するLangChainチャットボットの作成方法を説明します。PythonのLangChainライブラリとOpenAI GPT-4o LLM(大規模言語モデル)を使用して、自然言語クエリをGridDBクエリに変換し、データベースとシームレスにやりとりします。
ソースコードおよびJupyter Notebook
ソースコード(Jupyter Notebook)は、GitHubのリポジトリから入手できます。
$ git clone https://github.com/griddbnet/Blogs.git --branch chatbot前提条件
この記事のコードを実行するには、以下のライブラリをインストールする必要があります。 1. GridDB C Client 2. GridDB Python client
GridDB Python Package Index (Pypi) ページの手順に従って、これらのクライアントをインストールします。
また、LangChain、Numpy、Pandas、Seaborn ライブラリもインストールする必要があります。
以下のスクリプトは、このブログのコードを実行するために必要なライブラリをインストールし、インポートします。
!pip install langchain
!pip install langchain-core
!pip install langchain-openai
!pip install langchain-experimental
!pip install tabulateimport griddb_python as griddb
import pandas as pd
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.agents.agent_types import AgentType
from langchain_experimental.agents.agent_toolkits import create_pandas_dataframe_agent
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from typing import List, DictGridDBとの接続の作成
LangChainチャットボットでGridDBとやり取りするには、GridDBインスタンスとの接続を作成する必要があります。そのためには、get_instance()メソッドを使用して、StoreFactoryクラスのオブジェクトを作成する必要があります。次に、ファクターオブジェクトのget_store()メソッドを呼び出し、データベースのホスト名、クラスタ名、ユーザー、パスワードのパラメータを渡します。
次のスクリプトでは、GridDBインスタンスとの接続を行い、コンテナオブジェクトを作成することで接続が成功したかどうかをテストします。
factory = griddb.StoreFactory.get_instance()
DB_HOST = "127.0.0.1:10001"
DB_CLUSTER = "myCluster"
DB_USER = "admin"
DB_PASS = "admin"
try:
gridstore = factory.get_store(
notification_member = DB_HOST,
cluster_name = DB_CLUSTER,
username = DB_USER,
password = DB_PASS
)
container1 = gridstore.get_container("container1")
if container1 == None:
print("Container does not exist")
print("Successfully connected to GridDB")
except griddb.GSException as e:
for i in range(e.get_error_stack_size()):
print("[", i, "]")
print(e.get_error_code(i))
print(e.get_location(i))
print(e.get_message(i))
出力:
コンテナが存在しません GridDBに正常に接続しました
接続に成功すると、上記のメッセージが表示されます。接続に失敗した場合は、認証情報を確認して再度接続してください。
GridDBへのサンプルデータの挿入
GridDBコンテナから情報を取得するチャットボットを作成します。
ここでは、1970年から2022年までの各国の人口統計情報を格納したGridDBコンテナを作成します。このデータセットの詳細については、以前の記事world population data analysis using GridDBを参照してください。
また、Kaggleからデータセットをダウンロードすることもできます。以下のスクリプトでは、ダウンロードした「world_population.csv」をPandas DataFrameに読み込んでいます。
## Dataset link: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/iamsouravbanerjee/world-population-dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv(r"/home/mani/GridDB Projects/world_population.csv")
print(dataset.shape)
dataset.head()出力:
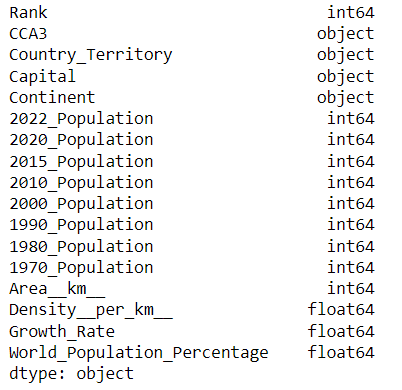
データセットには、国別人口、首都、大陸などの情報が含まれていることがわかります。
データセットの列には特殊文字が含まれていますが、GridDBでは列名に特殊文字を使用できないため、削除する必要があります。
dataset.columns = dataset.columns.str.replace('[^a-zA-Z0-9]', '_', regex=True)
dataset.dtypes出力:
次に、GridDB対応のカラムタイプにDataFrameのカラムをマッピングしてから、GridDBコンテナにデータを挿入します。
次のスクリプトは、dataset DataFrameのデータをPopulationStats GridDBコンテナに挿入します。
# see all GridDB data types: https://docs.griddb.net/architecture/data-model/#data-type
def map_pandas_dtype_to_griddb(dtype):
if dtype == 'int64':
return griddb.Type.LONG
elif dtype == 'float64':
return griddb.Type.FLOAT
elif dtype == 'object':
return griddb.Type.STRING
# Add more column types if you want
else:
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported pandas type: {dtype}')
container_columns = []
for column_name, dtype in dataset.dtypes.items():
griddb_dtype = map_pandas_dtype_to_griddb(str(dtype))
container_columns.append([column_name, griddb_dtype])
container_info = griddb.ContainerInfo("PopulationStats",
container_columns,
griddb.ContainerType.COLLECTION, True)
try:
cont = gridstore.put_container(container_info)
for index, row in dataset.iterrows():
cont.put(row.tolist())
print("All rows have been successfully stored in the GridDB container.")
except griddb.GSException as e:
for i in range(e.get_error_stack_size()):
print("[", i, "]")
print(e.get_error_code(i))
print(e.get_location(i))
print(e.get_message(i))出力:
すべての行がGridDBコンテナに正常に格納されました。
サンプルレコードを含むGridDBコンテナを作成したので、サンプルデータコンテナから情報を取得できるLangChainチャットボットを作成します。
GridDBデータとやりとりするLangChainチャットボットの作成
LangChainでは、幅広い大規模言語モデル(LLM)を使用してチャットボットを作成できます。今回は、OpenAIの最新LLMであるGPT-4oを使用してLangChainチャットボットを作成します。
LangChainでGPT-4oを使用するには、ChatOpenAIクラスのオブジェクトを作成し、OpenAI APIキーを渡す必要があります。
OPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
llm = ChatOpenAI(api_key = OPENAI_API_KEY ,
temperature = 0,
model_name = "gpt-4o")表形式データ用のチャットボットを作成する際のデフォルトLangChainチェーンの問題
前回の記事では、LangChainを使用したGridDBのCRUD操作の実行方法について説明しました。
その記事で使用したアプローチは、GridDBのコンテナとカラムの正確な名前が既知の場合に、自然言語を使用してGridDBとやり取りするのに適しています。そうでない場合、LLMは作成したカラム名を使用して情報を取得しようとします。
例えば、次のセクションでは、2020年の人口が最も多い上位3カ国の名前を取得しようとします。
class SelectData(BaseModel):
container_name: str = Field(description="the container name from the user query")
query:str = Field(description="natural language converted to SELECT query")
system_command = """
Convert user commands into SQL queries for Griddb.
"""
user_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_command),
("user", "{input}")
])
select_chain = user_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(SelectData)
def select_records(query):
select_data = select_chain.invoke(query)
container_name = select_data.container_name
select_query = select_data.query
print(select_query)
result_container = gridstore.get_container(container_name)
query = result_container.query(select_query)
rs = query.fetch()
result_data = rs.fetch_rows()
return result_data
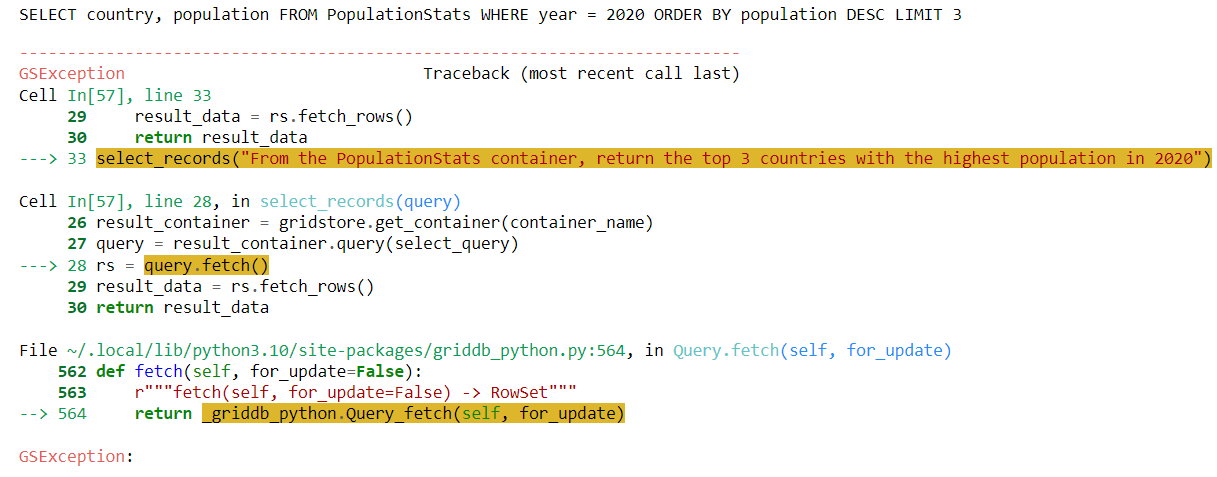
select_records("From the PopulationStats container, return the top 3 countries with the highest population in 2020")出力:
上記の出力から、LLMが country、population、および year 列から情報を返すクエリを生成していることが分かります。しかし、データセットを見ると、year 列は存在しません。代わりに、2020年の人口情報は 2020 Population 列に格納されています。
この問題を解決するには、LangChainエージェントを使用します。
表形式データとやりとりするためのLangChainエージェント
LangChainエージェントを使用するには、BaseModelクラスと、ユーザーのクエリからコンテナ名と追加のクエリ情報を抽出するselect_chainを定義します。
class SelectData(BaseModel):
container_name: str = Field(description="the container name from the user query")
natural_query:str = Field(description = "user query string to retrieve additional information from result returned by the SELECT query")
system_command = """
Convert user commands into SQL queries for Griddb.
"""
user_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_command),
("user", "{input}")
])
select_chain = user_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(SelectData)
次に、ユーザーのクエリを受け取り、コンテナ名と追加のクエリを取得するために select_chain を呼び出す select_records() 関数を定義します。 select_records() 関数は、Pandas DataFrame 内のコンテナデータを取得します。
次のステップは、OpenAIの create_pandas_dataframe_agent() を作成し、GridDBインスタンスからのコンテナデータを含むDataFrameを渡すことです。
追加のクエリは、エージェントの invoke() メソッドに渡されます。エージェントは、追加のユーザークエリに基づいてDataFrameから情報を取得します。
def select_records(query):
select_data = select_chain.invoke(query)
container_name = select_data.container_name
select_query = f"SELECT * FROM {container_name}"
natural_query = select_data. natural_query
print(f"Select query: {select_query}")
print(f"Additional query: {natural_query}")
result_container = gridstore.get_container(container_name)
query = result_container.query(select_query)
rs = query.fetch()
result_data = rs.fetch_rows()
agent = create_pandas_dataframe_agent(
ChatOpenAI(
api_key = OPENAI_API_KEY,
temperature=0,
model="gpt-4o"),
result_data,
verbose=True,
agent_type=AgentType.OPENAI_FUNCTIONS,
allow_dangerous_code = True
)
response = agent.invoke(f"Return the following information: {natural_query}")
return response
次のクエリを使用して、select_records メソッドをテストしてみましょう。PopulationStatsコンテナから、2020年の人口が最も多い上位3カ国を返す。
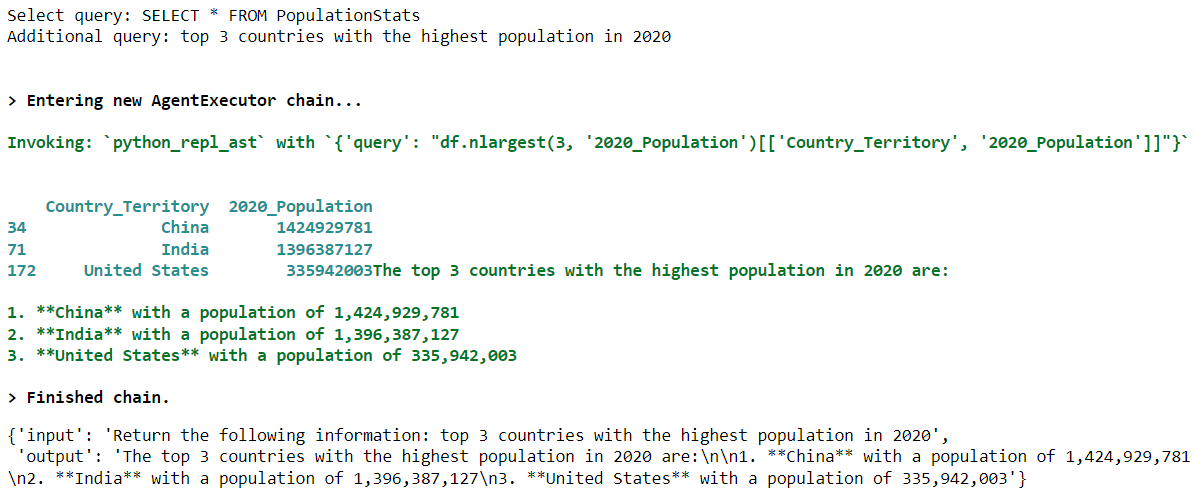
select_records("From the PopulationStats container, return the top 3 countries with the highest population in 2020")出力:
出力結果から、SELECT クエリが PopulationStats コンテナからすべてのレコードを選択し、追加のクエリが 2020 年の人口上位 3 カ国 を取得することがわかります。
上記の出力結果からわかるように、エージェントは対応する result_data DataFrame にアクセスでき、必要な情報を返すことができるため、PopulationStats コンテナのカラム名を知ることができます。
GridDBデータを使用したLangChainチャットボットの対話を構築
次に、前回の対話を記憶できるチャットボットを作成してみましょう。
前回のスクリプトのようにselect_records関数でエージェントを繰り返し定義するのではなく、DataFrameでコンテナ情報を取得し、そのDataFrameをエージェントで1回だけ使用することをお勧めします。
次のスクリプトでは、SelectData ベースクラスと、ユーザークエリからコンテナ名を取得する select_records() 関数を定義しています。
class SelectData(BaseModel):
container_name: str = Field(description="the container name from the user query")
query:str = Field(description="natural language converted to SELECT query")
system_command = """
Convert user commands into SQL queries for Griddb.
"""
user_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_command),
("user", "{input}")
])
select_chain = user_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(SelectData)
def select_records(query):
select_data = select_chain.invoke(query)
container_name = select_data.container_name
select_query = select_data.query
result_container = gridstore.get_container(container_name)
query = result_container.query(select_query)
rs = query.fetch()
result_data = rs.fetch_rows()
return result_data
result_data = select_records("SELECT all records from PopulationStats container")次に、ユーザーのクエリを受け取り、create_pandas_dataframe_agent エージェントを使用して Pandas DataFrame に関する情報を返す create_pandas_dataframe_agent および get_response() 関数を定義します。
チャットボットの機能を実装するには、get_response() 関数を呼び出し続け、エージェントの応答をコンソールに表示する while ループを実行する chat_with_agent() 関数を定義します。このループは、ユーザーが「bye, quit」または「exit」と入力すると終了します。
agent = create_pandas_dataframe_agent(
ChatOpenAI(
api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY,
temperature=0,
model="gpt-4"
),
result_data,
agent_type=AgentType.OPENAI_FUNCTIONS,
allow_dangerous_code=True,
)
def get_response(natural_query):
# Create a conversation chain
# Get the response from the agent
response = agent.invoke(f"Return the following information: {natural_query}")
# Add the interaction to the conversation memory
return response
# Function to chat with the agent
def chat_with_agent():
while True:
user_input = input("You: ")
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit', 'bye']:
print("AI: Goodbye!")
break
response = get_response(user_input)
print(f"AI: {response['output']}")
chat_with_agent()出力:
上記の出力から、GridDBコンテナから世界人口データセットに関する回答を取得するチャットボットのような機能を確認できます。
まとめ
本記事では、自然言語クエリを使用してGridDBデータと対話するLangChainチャットボットの作成方法について説明しました。PythonとGridDBの接続方法、GridDBコンテナへのサンプルデータの挿入方法、LangChainエージェントを使用した情報取得方法について説明しました。また、LangChainエージェントを使用したチャットボットの作成方法についても説明しました。
GridDBは、大量のリアルタイムデータを処理するように設計された、拡張性の高いNoSQLデータベースです。IoT(モノのインターネット)やビッグデータアプリケーションに最適です。GridDBは、高度なインメモリ処理機能と効率的な時系列データ管理機能を備えており、大量のデータセットを効果的に管理できます。
ブログの内容について疑問や質問がある場合は Q&A サイトである Stack Overflow に質問を投稿しましょう。 GridDB 開発者やエンジニアから速やかな回答が得られるようにするためにも "griddb" タグをつけることをお忘れなく。 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/ask?tags=griddb