このブログでは、GridDBのバッチ操作(マルチプットとマルチクエリー)を使ってアプリケーションのパフォーマンスを向上させる方法を紹介します。
マルチプット
バッチ書き込み操作は、過去に記録されたデータの一括読み込み、エッジデバイスからの複数のセンサー読み取り値の一度の入力、データコレクタ内での入力データの効率化のための意図的なキャッシュなど、さまざまな場面で使用されます。バッチクエリ操作は、マルチコンテナからデータをマージしたり、複数の集約操作を効率的に実施するのに使用されます。
シングルコンテナ
まず最初の例では、シングルコンテナに10,000行を一度に書き込んでみましょう。
blob = bytearray([65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74])
conInfo = griddb.ContainerInfo("col01",
[["name", griddb.Type.STRING],
["status", griddb.Type.BOOL],
["count", griddb.Type.LONG],
["lob", griddb.Type.BLOB]],
griddb.ContainerType.COLLECTION, True)
col = gridstore.put_container(conInfo)
i=0
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
while i < 10000:
row = [str(uuid.uuid1()), False, random.randint(0, 1048576), blob]
col.put(row)
i=i+1
print("single put took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングルプットでは上記のようになりますが、マルチプットでこれを最適化することができます。シングルプットで1つの行を10,000回書く代わりに、マルチプットで1,000行を10回書きます。
col = gridstore.put_container(conInfo)
i=0
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
rows=[]
while i < 10000:
rows.append([str(uuid.uuid1()), False, random.randint(0, 1048576), blob])
if i != 0 and i% 1000 == 0:
col.multi_put(rows)
rows=[]
i=i+1
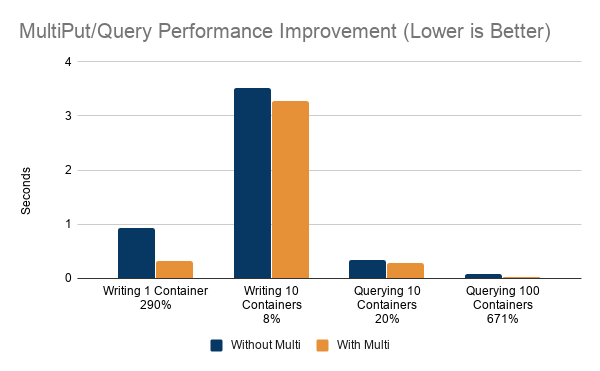
print("multiput put took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングルプットでは0.92秒だったのに対し、マルチプットでは0.32秒となり、290%もの改善が見られました。
マルチコンテナ
一般的に、マルチプットでマルチコンテナに書き込むのは、Kafkaのようなストリーミングプラットフォームを利用する時で、SinkコネクタやConsumerアプリケーション内で複数のセンサーのデータがコレクションとしてKafkaからフェッチされる場合です。
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
col = cols[no]
i=0
rows=[]
while i < 10000:
rows.append([str(uuid.uuid1()), False, random.randint(0, 1048576), blob])
if i != 0 and i% 1000 == 0:
col.multi_put(rows)
rows=[]
i=i+1
print("single container multi put took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")マルチコンテナをマルチプットで記述するには、gridstore.multi_put()で、コンテナ名をキーにしたマップを引数にします。
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
i=0
entries={}
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
rows=[]
i=0
while i < 10000:
rows.append([str(uuid.uuid1()), False, random.randint(0, 1048576), blob])
i=i+1
entries["col0"+str(no)] = rows
gridstore.multi_put(entries)
print("multi container multi put took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングルコンテナのマルチプットでは3.92秒でしたが、マルチコンテナのマルチプットではパフォーマンスが25%向上し、3.13秒となりました。
では、なぜマルチコンテナのテストはこれほど遅く、改善率も高くないのでしょうか。まず第一に、10倍のデータを書き込んでいるということで全体的な差は説明できます。改善率の低下はデータ転送のサイズが理由であると考えられます。最初のシングルコンテナ、シングルプットのテストでは、データ転送サイズが非常に小さいため、レコードあたりのオーバーヘッドが非常に大きくなっていますが、シングルコンテナ、マルチプットではデータ転送サイズが大きく、レコードあたりのオーバーヘッドはすでに小さくなっています。マルチコンテナにマルチプットしても、オーバーヘッドは大きく減少しません。
マルチクエリ
マルチクエリは通常、マルチコンテナのデータを1つのレポートで使用する場合に使用します。
10個のマルチコンテナ
一度にシングルコンテナを実行すると、次のようになります。
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
col = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
query = col.query("select *")
rs = query.fetch(False)
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("single container query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")gridstore.fetch_all() is used to query multiple containers:
queries=[]
col={}
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
col[no] = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
query = col[no].query("select *")
if query != None:
queries.append(query)
gridstore.fetch_all(queries)
for query in queries:
rs = query.get_row_set()
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("multi container query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングルコンテナのクエリにかかった時間は0.34秒、マルチコンテナのクエリにかかった時間は0.28秒と、20%の改善が見られました。
100個のマルチコンテナ
100個のコンテナを1行ずつ返すクエリで検索する場合、マルチプットなしでは次のようになります。
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
col = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
query = col.query("select * limit 1")
rs = query.fetch(False)
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("single container query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")マルチクエリを使うと、
queries=[]
col={}
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]:
if col.get(no) == None:
col[no] = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
query = col[no].query("select * limit 1")
if query != None:
queries.append(query)
gridstore.fetch_all(queries)
for query in queries:
rs = query.get_row_set()
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("multi container query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングルコンテナのクエリが0.04秒だったのに対し、マルチコンテナのクエリは0.01秒と、671%もの高速化を実現することができました。
集計
マルチクエリなしでは、
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]:
col = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
for agg in [ "min", "max", "avg", "count", "stddev"]:
query = col.query("select "+agg+"(count) ")
rs = query.fetch(False)
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("single aggregation query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")マルチクエリを使用すると、
queries=[]
col={}
start = datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp()
for no in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]:
if col.get(no) == None:
col[no] = gridstore.get_container("col0"+str(no))
for agg in [ "min", "max", "avg", "count", "stddev"]:
query = col[no].query("select min(count)")
if query != None:
queries.append(query)
gridstore.fetch_all(queries)
for query in queries:
rs = query.get_row_set()
while rs.has_next():
data = rs.next()
print("multi aggregation query took "+ str(datetime.datetime.utcnow().timestamp() - start) +" seconds")シングル集計のクエリが0.08秒であったのに対し、マルチ集計のクエリは0.06秒と、39%の改善が見られました。
結論
マルチプットとマルチクエリを使うことで、GridDBアプリケーションのパフォーマンスを飛躍的に向上させることができます。どの程度パフォーマンスを向上させることができるかについては注意が必要です。
マルチプット、マルチクエリがパフォーマンスをどの程度向上させることができるかは、プットとクエリのデータの量によって決まります。それぞれのプットとクエリが大量のデータを転送する場合、得られるパフォーマンスの量は減少します。これまでの例を見ると、GridDBのデータブロックサイズ(デフォルトでは64kb)を超えるデータを転送するリクエストでは、パフォーマンスの向上が見込めなくなることが分かりました。また、余分な計算を必要とするクエリ(where-claus、order by、aggregationなど)も、マルチクエリのパフォーマンスに影響を与えます。
If you have any questions about the blog, please create a Stack Overflow post here https://stackoverflow.com/questions/ask?tags=griddb .
Make sure that you use the “griddb” tag so our engineers can quickly reply to your questions.